HVTS vs. Twin Wire Arc Spray – What’s the Difference?

Twin wire arc spray (TWAS) and High Velocity Thermal Spray, HVTS Solution are both thermal spray processes used for applying metal alloy cladding to surfaces, but they differ in terms of technology, bond strength, application speed, cost and maintenance requirements.
Key Difference Between HVTS℠ and Twin Wire Arc Spray
1. Operational Differences
HVTS
HVTS employs a proprietary wire feedstock atomized within a supersonic gas stream. This process yields a cladding characterized by a unique blend of high density, low porosity, and strong bonding. Consequently, HVTS is well-suited for applications demanding superior resistance to corrosion and erosion under challenging conditions.
Twin Wire Arc Spray
Twin Wire Arc Spray utilizes regular off the shelf wire feedstock atomized in a low velocity gas stream and propelled onto the substrate. The resulting cladding has high oxide levels, internal stress, low adhesion, porosity and permeability, which is suitable for aluminum/zinc sacrificial coatings.
2. Particle Velocity
HVTS
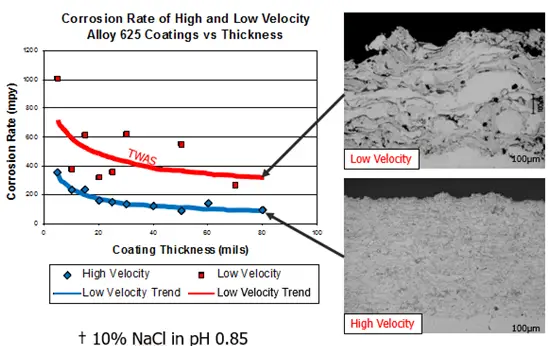
This process is specifically characterized by the high velocity of the sprayed particles, which contributes to the coating’s high density and adhesion to the substrate. In comparison to TWAS, HVTS can be advantageous in applications where minimizing oxidation and internal stress of the coating material is crucial. The higher velocities in HVTS improves the integrity of the sprayed material and corrosion barrier.
Twin Wire Arc Spray
While the velocity in Twin Wire Arc Spray is high, it is relatively much lower than in HVTS. The spraying process involves the molten material being propelled onto the substrate. Oxidation of molten particles happens extremely fast. This results in highly oxidized coatings.
3. Coating and Cladding Characteristics
HVTS℠
HVTS℠ Claddings are known for their high density, low porosity, and excellent bond strength. These characteristics make HVTS℠ suitable for applications where corrosion protection and wear resistance are critical.
Twin Wire Arc Spray
Twin Wire Arc Spray coatings typically exhibit good adhesion and can provide effective sacrificial protection. However, the density and porosity may vary depending on the specific parameters used in the spraying process. It is extremely hard to create an isolating coating with TWAS.
4. Applications
HVTS℠
HVTS℠ is often used in applications where extreme conditions such as high temperatures, corrosive environments, or abrasive wear are present. Industries like power generation, petrochemical, chemical, metals and mining, and oil and gas often employ HVTS for the protection of critical components and process assets.
Twin Wire Arc Spray
Twin Wire Arc Spray is inexpensive and finds applications in various industries, including automotive, marine, and general manufacturing. It is commonly used for sacrificial external corrosion protection, repair and improving the wear resistance of components.
Click here for a comprehensive comparison of IGS (HVTS) versus Twin Wire Arc Spray
Key Benefits of HVTS℠ over Twin Wire Arc Spray
1. Reduced Oxidation and Decarburization:
HVTS℠ is advantageous in applications where minimizing oxidation and decarburization of the coating material is crucial. The higher velocities of HVTS maintain the integrity of the sprayed material.
2. Greater Thickness Control
HVTS℠ provides better control over coating thickness. This can be important in applications where precise thickness specifications are required for optimal performance.
3. Wide Range of Materials
HVTS can be used with a variety of coating materials, including metals and alloys. This versatility makes it suitable for a broad range of applications where different material properties are needed.
4. Reduced Heat Input
HVTS℠ can be a lower-heat-input process compared to Twin Wire Arc Spray. This can be beneficial for applications where minimizing substrate heat input is critical, such as when coating temperature-sensitive materials.
5. Efficient Material Usage
HVTS℠ can be more efficient in terms of material usage, as the high velocities allow for better control and optimization of the coating material. This can lead to cost savings in terms of material usage.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision between HVTS℠ and Twin Wire Arc Spray should be informed by a thorough consideration of the specific demands of the intended application, considering factors such as material requirements, operational conditions, and cost considerations. Both processes offer benefits, allowing industries to tailor their coating solutions to meet the diverse challenges faced.
Comparison Table of IGS (HVTS) versus Twin Wire Arc Spray
High Velocity Thermal Spray
Conveyance Technology
High velocity system
Significant increase in performance (both erosion and corrosion resistance)
Lower porosity of <2%
Less coating stress
Low permeability
Twin Wire Arc Spray
Conveyance Technology
Low velocity system
Higher oxide content for interconnected oxides and increased porosity
Higher porosity of >25%
Greater coating stresses
High permeability