Robotic TubeTech™ De-fouling Enhances Oman Methanol Reformer Efficiency
Summary
Oman Methanol Company LLC (OMC), a major methanol producer in the Middle East, faced significant operational challenges due to fouling in their reformer furnace convection section. This case study examines how IGS Tube Tech’s robotic cleaning technology successfully restored optimal heat transfer efficiency, resulting in substantial operational and environmental benefits.
Plant Profile
Organization: Oman Methanol Company LLC (OMC)
Location: Sohar Industrial Port complex, Oman
Industry: Petrochemical Production
Capacity: 3,000+ tonnes
Established: 2004
Ownership: Oman Methanol Horizon Company LLC
and Methanol Holdings International Limited (MHIL)
Project Objectives
- Remove maximum deposit accumulation from external tube surfaces
- Complete the cleaning process within the shortest possible timeframe
- Implement the safest cleaning methodology available
- Restore optimal heat transfer efficiency
- Reduce fuel consumption and emissions
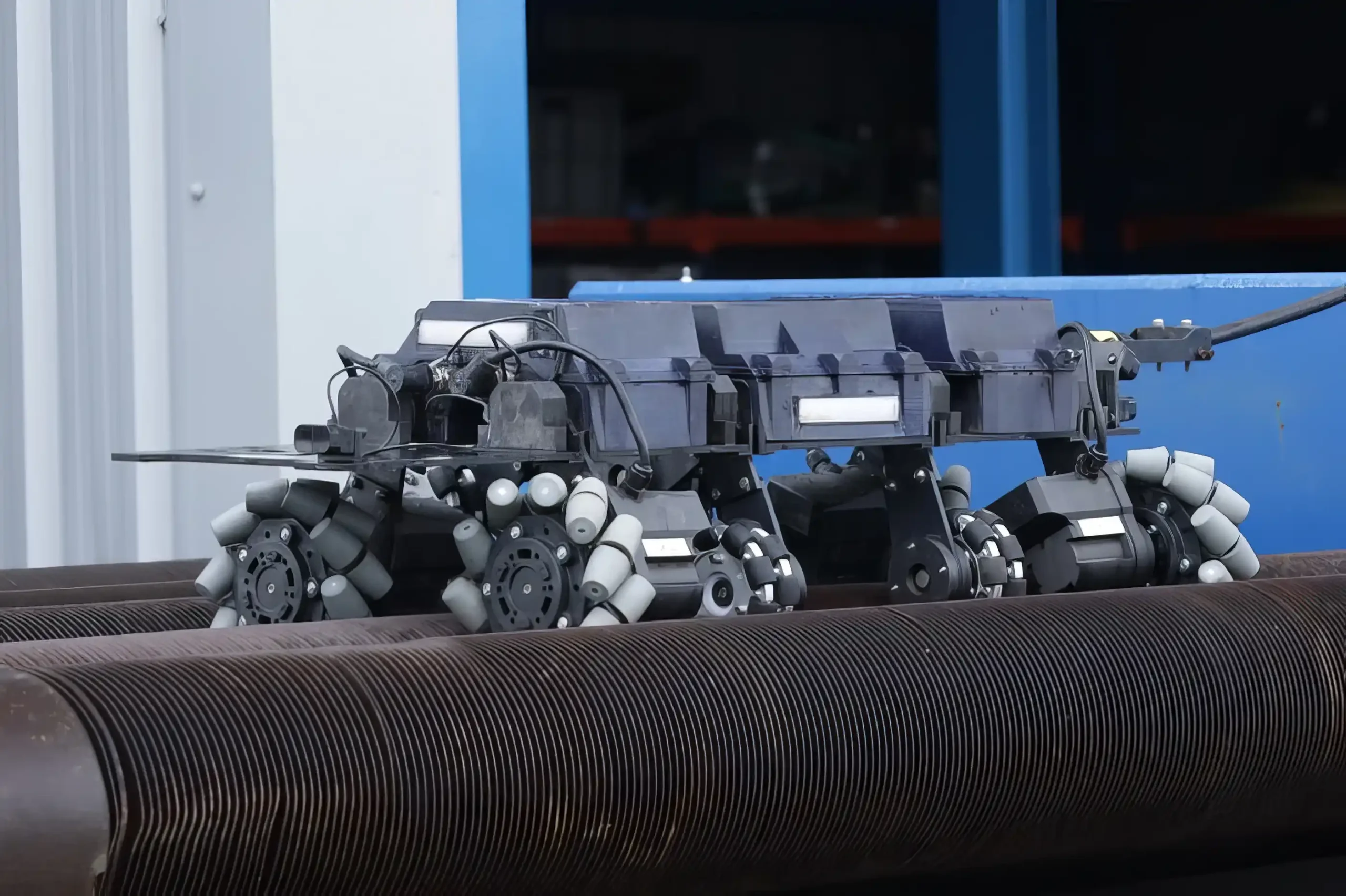

Efficiency Challenge in Reformer Convection Section
The convection section of OMC’s Reformer developed significant fouling on the external surfaces of finned tubes over time. This accumulation created several critical operational issues:
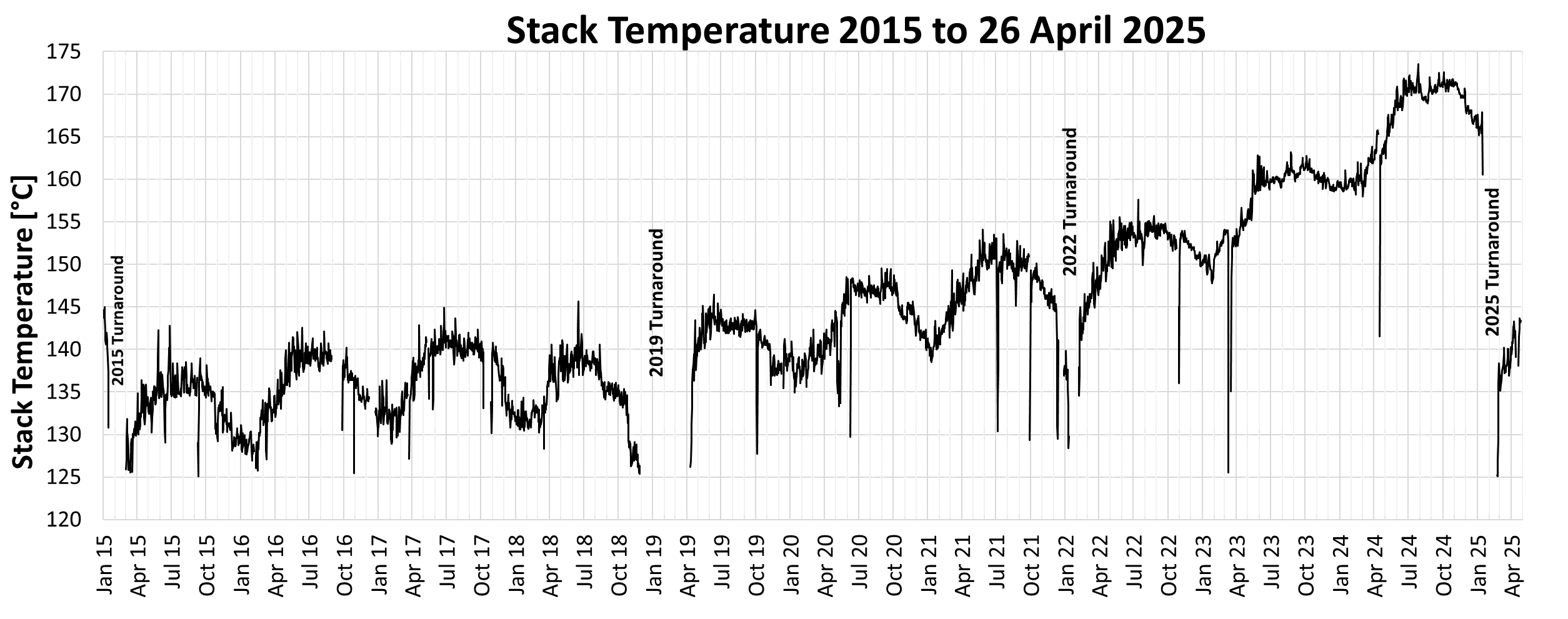
- Elevated Stack Temperatures: temperatures reached 168°C / 320°F, significantly exceeding the optimal 135°C / 275°F target.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: reduced heat recovery necessitated higher fuel input.
- Restricted Production Capacity: the facility was limited to operating at only 93–95% of its designed capacity and was not able to reach desirable superheated steam temperature.
- Maintenance Complexity: the fouled areas presented accessibility challenges for conventional cleaning methods.
Solution Implementation
IGS deployed its latest TubeTech™ robotic cleaning technology, specifically engineered to tackle heavy fouling in heat exchange equipment.
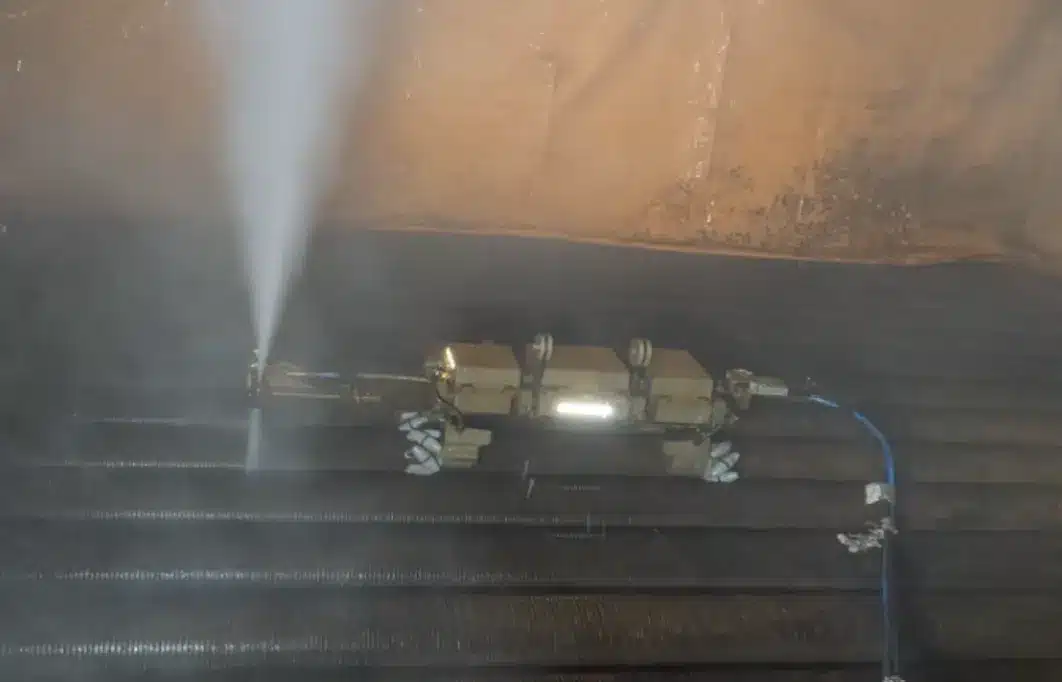

The implementation focused on a reformer, with the technicians strategically utilizing two existing access windows while creating two additional access points to effectively reach banks two and four.
This remote operation approach eliminated the need for hazardous confined space entry by personnel, while enabling precision cleaning that specifically targeted the finned tube external surfaces where fouling accumulation was most severe, ensuring optimal cleaning efficiency throughout the critical heat transfer zones.
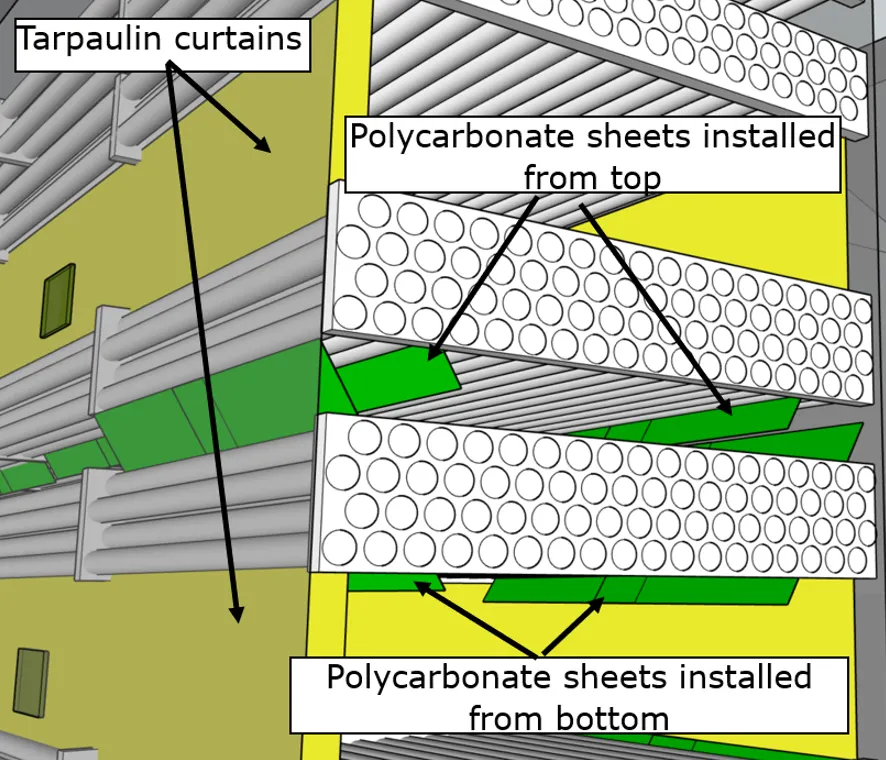
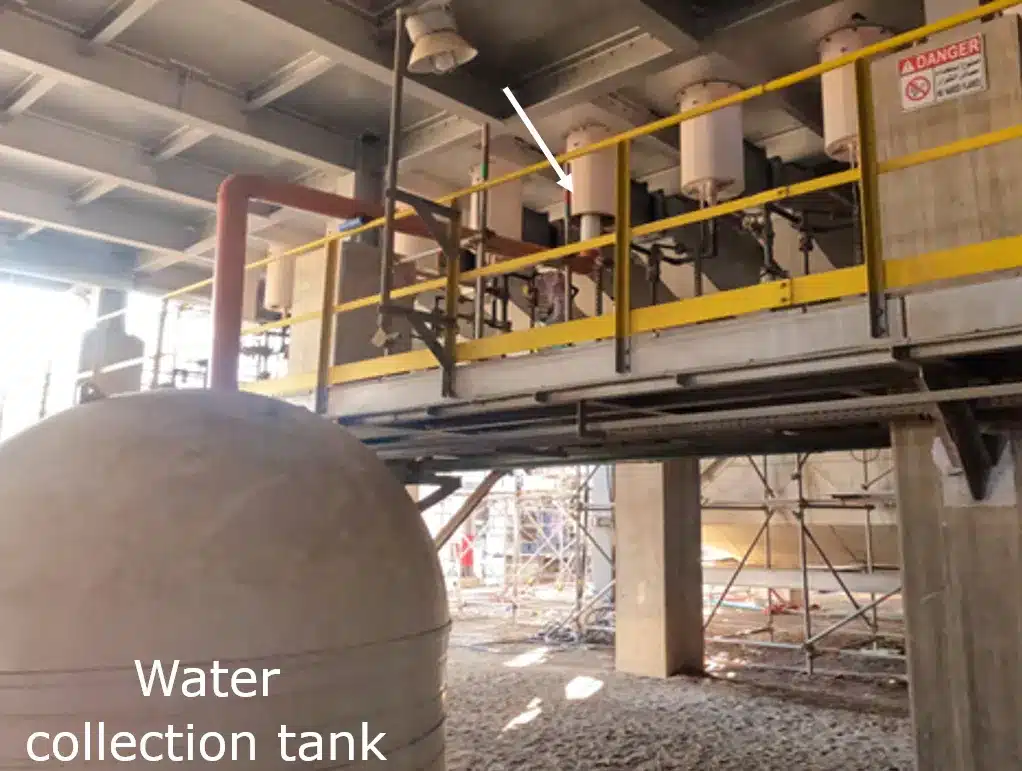
Along with additional doors, to prevent any potential impact on old refractory and allow more efficient effluent collection, a set of tarpaulin curtains and plastic boards (Figure 4) was designed.
Also, several burners from the superheater section were pulled out to install drainage pipes and effectively collect cleaning media.
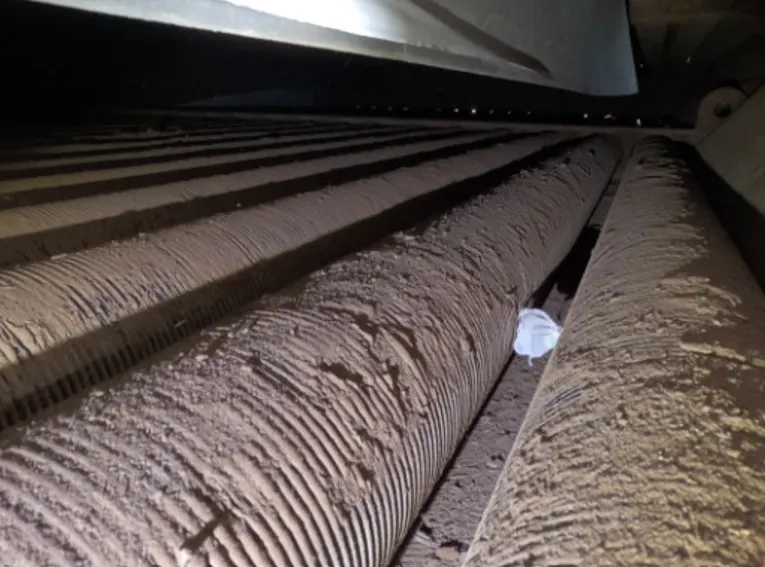


Results and Benefits
Following the cleaning operation, the plant experienced significant measurable improvements as 34 °C / 93.2°F stack temperature reduction was achieved, allowing a 1.8% gain in total fuel efficiency of the primary methanol reformer. These improvements delivered multiple operational benefits, including a reduction in fuel consumption that significantly enhanced energy efficiency across the asset. Environmental impact was minimized through lower emissions resulting from improved combustion efficiency, while production was restored
and the plant went back to full throughput capacity.
Economic benefits materialized through reduced operating costs driven by substantial fuel savings, and sustainability was advanced through enhanced overall plant efficiency, creating a more environmentally responsible operation with a smaller carbon footprint.
Long-Term Impact
Based on the successful outcomes, the plant has:
- Committed to incorporating routine robotic cleaning into their regular maintenance schedule
- Expressed interest in further collaboration with IGS for refractory encapsulation solutions
- Established a new operational best practice for maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency
Conclusion
The implementation of IGS TubeTech’s robotic cleaning technology at Oman Methanol’s facility demonstrates the significant value of advanced maintenance solutions in the petrochemical industry.
By restoring optimal heat transfer efficiency, the project delivered measurable operational, economic, and environmental benefits while establishing a foundation for sustained performance improvement.
TubeTech™ Fouling Removal Services
Heat Exchanger Fouling Removal Services:
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Fouling Removal
- Fired Heater Furnace Fouling Removal
- Texas Tower (VCFE) Fouling Removal
- Twisted Tube Heat Exchanger Fouling Removal
- U-Tube (Hairpin) Heat Exchanger Fouling Removal
Air Cooled Condenser Fouling Removal (ACC)
Fouling Removal for Inspection:
Free consultation with an IGS Subject Matter Expert
IGS is here to provide information, answer questions and create an effective solution for your needs.
